Possible Negative Effects
- Devices – from Smart Phones to Tablets to Laptops to Nintendo Switch to TV’s, it is extremely easy to be carried away about ‘Screen Time’ and completely worried about the amount of time children and young adults are spending staring at device screens .
- More & More pupils are discussing issues with SLEEP, DEPRESSION, ANXIETY & FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
- Online Safety remains using dialogue with your children & young adults, and not about denying usage.
- Certainly, as a last resort, denying access can work but before you get that far, try my Online Safety Top Ten Tips.
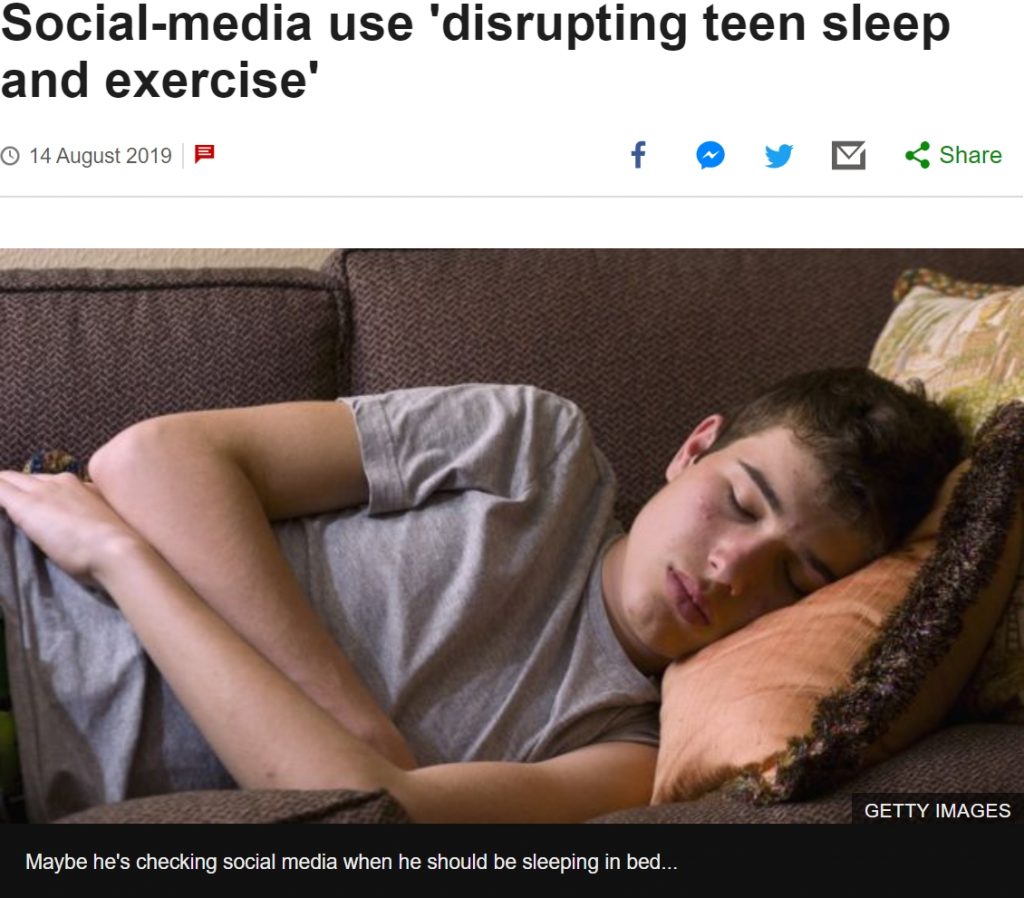
Using social media is not directly harming teenagers – but it can reduce the time they spend on healthy activities, such as sleeping and exercising – UK BBC
The American Academy of Paediatrics has warned about the potential for ‘negative effects of Social Media in young children and young adults – including Online Bullying – US FORBES
Social Media / Gaming Positive Effects – Speaks Up – Connects with others – Making new friends – Communicating – Direct Messaging – Emailing – Texting
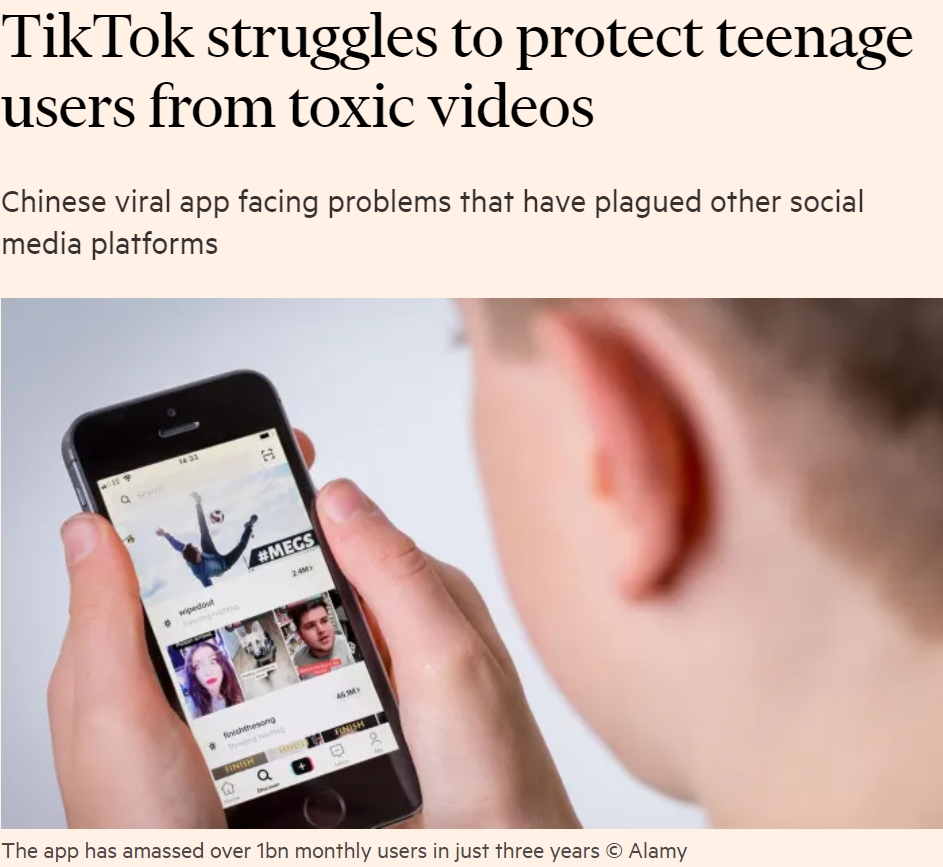
Social Media / Gaming Negative Effects – Consuming Time – Scrolling – FOMO – Watching Tik Tok – Watching Snaps – Watching Games – SELF COMPARISON
Possible Negative Effects (cont)
Survey results found that Snapchat, Facebook, Twitter & Instagram all led to increased feelings of depression, anxiety, poor body image and loneliness. Too much passive use of Social Media – just browsing posts- can be unhealthy & has been linked to feelings of ‘envy, inadequacy & less satisfaction with life. Studies even suggested that it can lead to ADHD symptoms, depression, and sleep deprivation.
A recent survey of almost 1,500 young people (aged 14-24) from across the UK asked them to score how each of the social media platforms they use impacts upon 14 health and wellbeing-related issues which were identified by experts as the most significant.
The Main Health and Wellbeing-related issues :
- Anxiety -feelings of worry, nervousness or unease
- Depression – feeling extremely low and unhappy
- Loneliness – feelings of being all on your own –
- Sleep – quality and amount of sleep
- Self-expression – the expression of your feelings, thoughts or ideas
- Self-identity – ability to define who you are
- Body Image – how you feel about how you look
- Real World Relationships – maintaining relationships with other people
- Community Building – feeling part of a community of like-minded people
- Bullying – threatening or abusive behaviour towards you
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) – feeling you need to stay connected because you are worried things could be happening without you.
Advice & Guidance
12-17-Year-Old Social Media Statistics
91% of 16–24-year-olds use the Internet for Social Media & Gaming
Social Media & Gaming use is linked with increased rates of anxiety, depression and poor sleep
Social Media & Gaming has been described as more addictive than cigarettes and alcohol
Best & worst Social Media Apps for ‘mental Health ?
BEST – You Tube / Twitter / Facebook WORST – Instagram / Snapchat / Tik Tok / Discord / Steam
What age should a student be on Social Media
Ages 0 – 13 – Private
Age 12 – Parents should have a discussion with your child and explain what their online brand should look like – Be Proud
Age 13 – Parents should consider a signed Social Media & Gaming Use Contract / Online Safety Screen Plan
Age 13 – 15 – Start building a personal portfolio, use positive personal photos and posts. Use Instagram, Snapchat, Tik Tok as an extension of the personal online brand not the sole personal brand.
Age 14 – 15 Publish the portfolio as a website & / or Blog to improve Google results
Age 17- Schools should discuss Positive Digital Tattoos for Universities and future employment.
What age should a child have their own Smart Phone
Ages 0 – 10 – No Phone – No need
Age 10-13 – ‘Brick Type’ Phone, that allows for SMS, text messaging and managed phone calls.
Age 13 – Parents should consider a signed Smart Phone Contract
Age 14 – Consider a Smartphone (without Social Media installed), use Google Family Link (Android) & Family Sharing (Apple).
Age 15- Smartphone with Social Media & Gaming Apps installed
What can Parents / Trusted Adults Do ?
- Remind all children and young adults that they can always come to them for help, guidance, and advice. Important they show themselves as ‘responsible’ before setting up their own profiles.
- Use the Online Safety Ten Top Tips for Parents & Ten Top Tips for Young Users to maintain an appropriate use of Social Media & Gaming sites and Apps.
- Use the Apps and Sites resource to understand the possible issues and harm that may occur
What Parents & Carers can do – Important Steps to Keep Children Safe Online
- During COVID- 19, virtual schooling, lockdown and excessive internet access, parents, carers trusted adults must speak openly with their children, about the dangers of social media, and online predators, parents can better prepare children for the dangers of online activity.
- Make sure that your child only interacts, messages, and engages with ‘True Friends’. True friends are friends who do not ask personal questions e.g., Family, cousins, school friends and outside school friends.
- It is essential to have security settings in place. Parents should also monitor their child’s social media activity by becoming “friends” or following them on various social media accounts and being present while kids are using social media in the house.
- Whenever possible, make sure the location services on your child’s phone or individual apps are disabled. This is especially so for Instagram, Facebook, Twitter etc, as it is possible to establish exactly where the most common place is, that your child posts from (i.e., Home)
- Always Check on Live Streaming – choosing a generic screen name and profile picture, that hides a child’s identity is a must. Additionally, in the live streaming App, it is important for parents to monitor their child’s live broadcasts to keep things in check by passively watching.
- Speak to School Principal, the School Designated Safeguarding Lead, or the Class Teacher.
Jonathan Taylor MSc www.onlinesafety4schools.co.uk besafeonline@ymail.com
